

Exploring these concepts in depth and learning how they apply to real-world situations might be fun for some people.
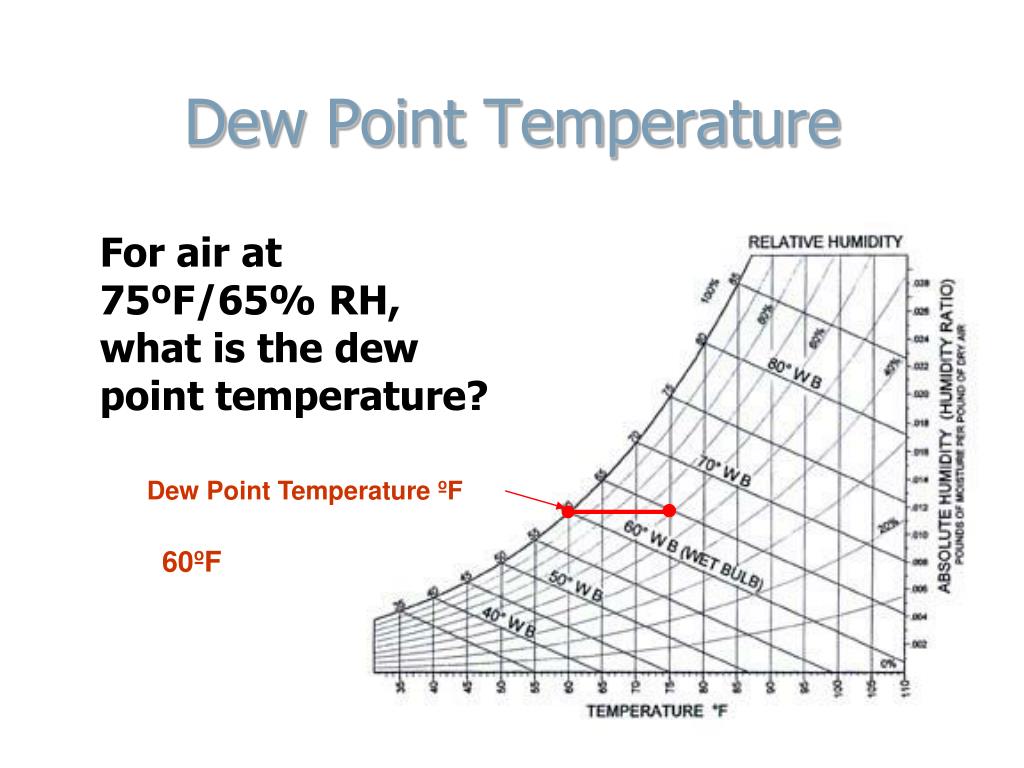
People can make informed decisions about farming, gardening, and outdoor recreation by understanding dew point.ĭew point is also a fascinating exercise in scientific inquiry, since it involves understanding air, water, and temperature properties. Weather forecasting, air conditioning, and plant growth can all be affected by this. Water vapor in the air condenses at the dew point. If you're a bit interested in meteorology, environmental science, or agriculture you may find this interesting. In case of vapour absorption system, rectifier is a cooling coil, which cools water vapours below dew point temperature.For a quick definition dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with respect to a plane surface of water.Practical Applications of Dew Point Temperatureįollowing are the practical applications of dew point temperature. Therefore, for saturated air, all three temperatures, namely dry bulb temperature, wet bulb temperature and dew point temperature are same. relative humidity is 100%), then wet bulb depression as well as dew point depression becomes zero. If the temperature of air becomes equal to or less than dew point temperature, then water will leave the air and air will be dehumidified.When the moisture content remains constant and temperature goes on increasing, then relative humidity and hence, difference between dry bulb temperature and dew point temperature goes on decreasing.It means that, air has diffused maximum amount of water vapour (moisture) into it. Air is said to be saturated air, if its relative humidity is 100 %.Air having 100% relative humidity indicates that, its dew point temperature is equal to its dry bulb temperature.Air having a high relative humidity indicates that, its dew point temperature is closer to its dry bulb temperature.The dew point temperature is associated with relative humidity.This condition is represented by point ‘B’ in Fig. Note: When the partial pressure of water vapour (p v) is equal to the pressure (p s) corresponding to saturation temperature, then the water vapour is in the saturated condition and the air will be saturated air. Thus, the temperature, at which, water vapour begins to condense is called as dew point temperature. Further cooling will result in condensation of water vapour along constant temperature line, i.e. t dp = t sat. At this point ‘B’, first drop of dew is formed and hence, the temperature at this point is called as dew point temperature. Now, if we cool the mixture at constant partial pressure shown by curve A-B the water vapour will be cooled, until it reaches the saturated state shown by point. Thus, the water vapour in air exists in the superheated state and moist air containing moisture in superheated state is said to be unsaturated air. As the value of p v is very small, therefore saturation temperature corresponding to ρ v is very small and even less than dry bulb temperature. In other words, the dew point temperature is the saturation temperature (t sat) corresponding to the partial pressure of water vapour (p v).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
